PTFE tubing — which stands for poly-tetra-fluoro-ethylene — offers several beneficial properties that make it incredibly advantageous for a variety of industrial applications. It is non-flammable, for instance, which makes it ideal for use in high-temperature settings such as an aircraft. In fact, PTFE’s properties are so numerous you can find the tubing in use across many industries like aviation, medical, automotive, electrical, food and beverage and even standard science or chemistry.
More commonly, the tubing is in use within HVAC and air-cooling systems because of its variable temperature compatibility. It can withstand drastic temperature changes in either direction, making it suitable for the kind of ductwork conducive to heating and cooling systems.
We’re going to take a closer look at some of the ways to use PTFE components and materials, as well as the benefits it can offer in each situation.
8 Industries That Incorporate PTFE Tubing
Here are some of the industries that currently leverage PTFE tubing and materials.
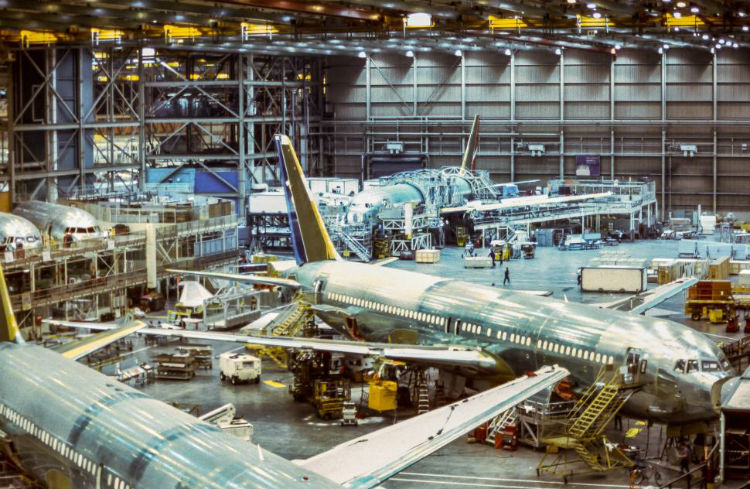

1. Aviation and Aircraft
The non-flammable and temperature-resistant fluoropolymers in PTFE tubing exhibit what’s called a lower friction coefficient. In addition to extreme temperatures, this makes PTFE tubing resistant to radical pressure changes. Therefore, the tubing is common in aviation, specifically to wrap or house wiring and cables that would otherwise be exposed.
2. Automotive
As in aviation, the durable properties of PTFE tubing make it ideal for use in automobile engines, which are subject to variable temperatures. The fuel system, for example, needs a reliable way to pass through — PTFE is excellent for fuel evaporation and fuel rail systems. The low gas permeability of PTFE tubing — thanks in part to that low friction coefficient — means it can contain the fuel even in evaporated forms.
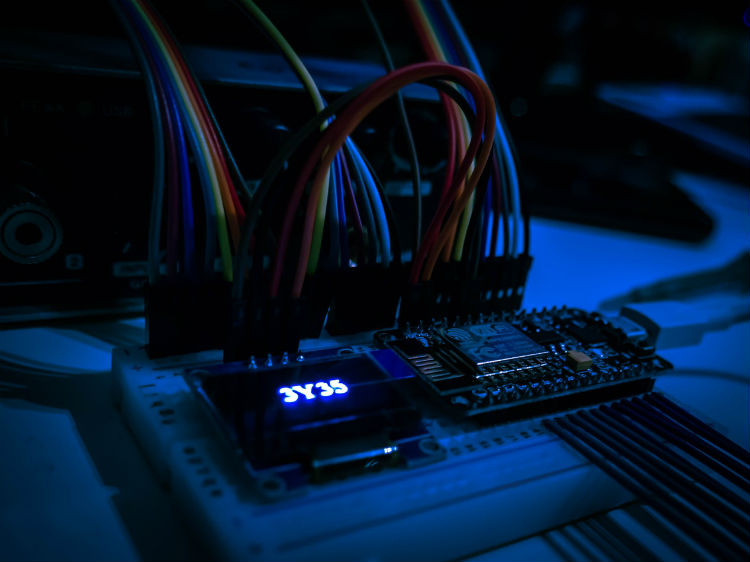

3. Electrical
Wiring and cables that are integral to the operation of most electronics can be decidedly fragile. Naturally, it’s common to see the components protected by high-quality Teflon PTFE tubing that can handle high temperatures, is not conductive and resists physical damage, too.
4. Medical
Nearly every medical device or apparatus requires some form of tubing, whether to inject chemicals and medicine, or to drain bio-fluids. PTFE tubing is in use to this end for drainage tubes, ventilators, protective tubing and even to disperse artificial tissues. When comprised of Teflon, it can also be used directly in biochemical and medical applications inside the human body.
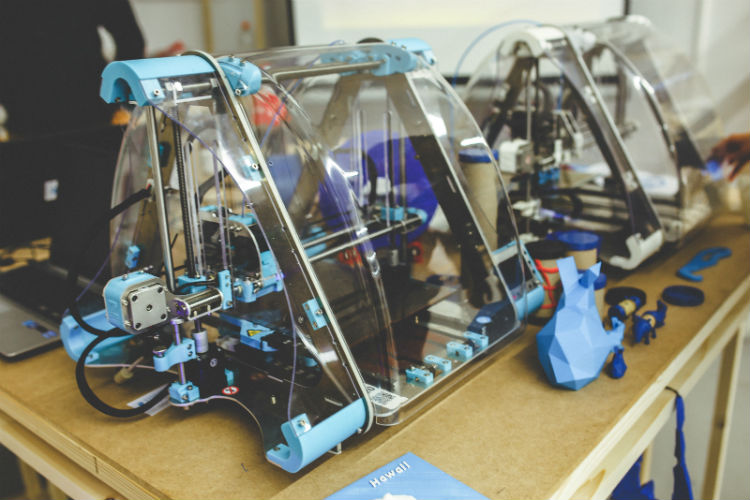

5. 3D Printing
Inherently, 3D printers need a high-temperature resistant tubing to transfer filament to the nozzle and printing area. Filament — most commonly an ABS plastic composite — gets heated to a more malleable state and fed through a small nozzle at the top of the printer. The computer system then tells the press how and where to inject the material. The problem is that the filament must pass from the heating element to the nozzle and into the printing area by way of tubing.
As you might have guessed, PTFE and Teflon tubing are ideal for such an application, due to their high-temperature properties and smooth makeup. The low friction coefficient means filament will slide through with no resistance whatsoever.
6. Textile
Believe it or not, many of the textiles in commercial and consumer-level goods must be manipulated, cleaned or combined with chemicals first. However, such chemicals can cause severe corrosion in conventional pipes. Teflon TPFE and PTFE tubing, which can withstand the corrosive properties of the chemicals passing through, can substitute for more conventional methods. Such tubing is also useful for textile rollers, which must be able to withstand extremely high temperatures and variable pressure changes.

7. Food and Beverage
As in the medical industry, any tubing or materials that transfer and produce foods must be able to resist external contamination. Furthermore, when chemicals or foods pass through the tubing, nothing gets left behind, thanks to the low coefficient which creates a remarkably smooth surface. That allows food manufacturers to process and combine various foods and chemicals in a reliable and consistent environment.
8. Fiber-Optics
While not necessarily a large-scale industry by itself — fiber-optics falls more in line with communications and networking — such cables are in use for a variety of applications. High-speed Internet systems and networks, for example, rely on fiber-optic sources to facilitate rapid and expansive data transfers.
The extremely delicate fibers within a greater fiber-optic cable can cause severe problems if they become severed or damaged, so it’s necessary to surround them with suitable protection. PTFE tubing is naturally lubricated because the surfaces are so smooth, which makes it ideal for the storage of fiber-optic cables, especially since it can withstand high temperatures and physical damage.
Plus, the PTFE material is easy to form into varying shapes and sizes, which is certainly necessary when running cabling or wire throughout structures, roadways and environments.
Tips for Working With PTFE Tubing and Materials
Due to its remarkably durable properties, PTFE tubing must be properly handled, especially if the goal is to bond it to another material or surface. For example, chemical etching alters the surface property of the tubing so it will mold, glue or bond better with alternate materials. Without etching, you cannot bond PTFE tubing.
The storage of etched tubing is also a problem because the process is impermanent. If left unused for long periods, the tubing will return to normal, thus losing its bondability. It will need to be re-etched if you hope to bond it to another material or surface.
Furthermore, PTFE tubing requires precision cuts if you need to reduce it in size. You can use household tools, but this will often result in the development of something called a burr — a rough edge that forms on the edge of manually cut piping. Such cuts can also reduce the reliability of the durable properties, so it’s best to use professional tools or hire a professional outright. Clamping or bending the tubing, for instance, can weaken the material at the affected ends.
In the end, it’s apparent that despite its rather restrictive handling requirements, PTFE tubing is useful for many applications across a swath of industries. It serves as a suitable alternative to more conventional forms of tubing and materials — especially since it can resist extreme temperatures, pressure, corrosion, physical damage and contamination.